library(tidyverse)
library(gt)
library(mgcv)
all_tetanus <- readRDS("data/preprocessed/all_samples.rds")Tetanus sero data
Concentration
There is currently no specific threshold to classify tetanus serostatus, for this analysis, a conservative threshold of 0.1IU/ml is used.
# threshold to be considered positive
positive_threshold <- 0.1Preprocess data
Label whether it is oucru or hcdc sample
Label the collection period for samples from each source
Compute rounded age
Compute concentration
- Use
medianvalue to compute where available, uselowerorupperotherwise - Concentration is computed by
titer*dilution_fctwhere titer is the predicted “concentration” from the standard curve.
- Use
Label whether the sample is considered positive using 0.1IU/ml threshold
- If concentration is not available –> the OD is either too high or too low, in which case seropositivity is determined by which extreme it is closer to (i.e., if OD closer to 0, label as negative and label as positive when OD is closer to 4)
Also filter samples from HCMC only
Code for preprocessing data
preprocessed_data <- all_tetanus %>%
mutate(
log_concentration = case_when(
!is.na(median) ~ median,
!is.na(upper) ~ upper,
!is.na(lower) ~ lower,
.default = NA
),
concentration = (10^log_concentration)*dilution_factors,
serostatus = if_else(
!is.na(concentration),
# if concentration available, determine positivity using threshold
if_else(concentration >= 0.1, "positive", "negative"),
# if concentration not available, determine positivity using OD
# if result closer to OD upper bound, it is positive
if_else((4 - result) < (result - 0), "positive", "negative")
),
source = if_else(str_detect(sample_id, "^U"), "hcdc", "oucru"),
age = case_when(
!is.na(dob) ~ as.double(difftime(date_collection, dob, unit = "days"))/365.25,
!is.na(exact_age) ~ exact_age,
!is.na(age_min) ~ age_min,
!is.na(age_max) ~ age_max,
.default = NA
),
rounded_age = round(age)
) %>%
filter(
province %in% c("HCMC", "Hồ Chí Minh", "HỒ CHÍ MINH")
) %>% group_by(source) %>%
mutate(
time_durr = paste0(
format(min(date_collection), "%Y/%m"),
" - ",
format(max(date_collection), "%Y/%m"))
) %>%
ungroup() Different dilutions
Visualize distribution of concentration at different dilution levels and the positive threshold
Plot distribution of log concentration at different dilutions
preprocessed_data %>%
ggplot() +
geom_density(
aes(
x = concentration,
color = time_durr
)
) +
geom_vline(
aes(
xintercept = positive_threshold
),
color = "green",
linetype = "dashed"
) +
scale_x_log10() +
facet_wrap(~ dilution_factors) +
labs(
color = "Collection period"
)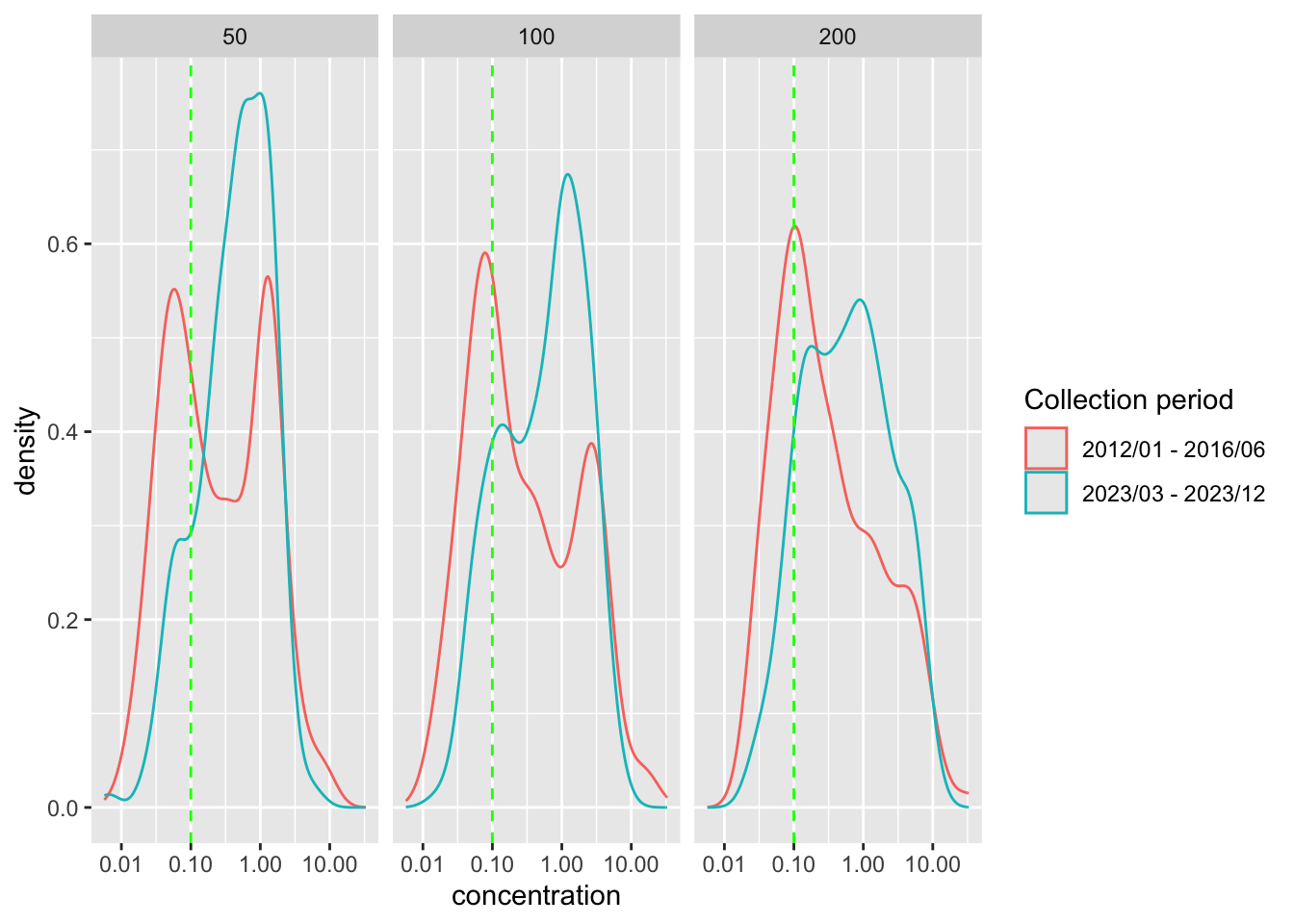
# which dilution factor for the following analyses
dilution_fct <- 200Concentration by collection period
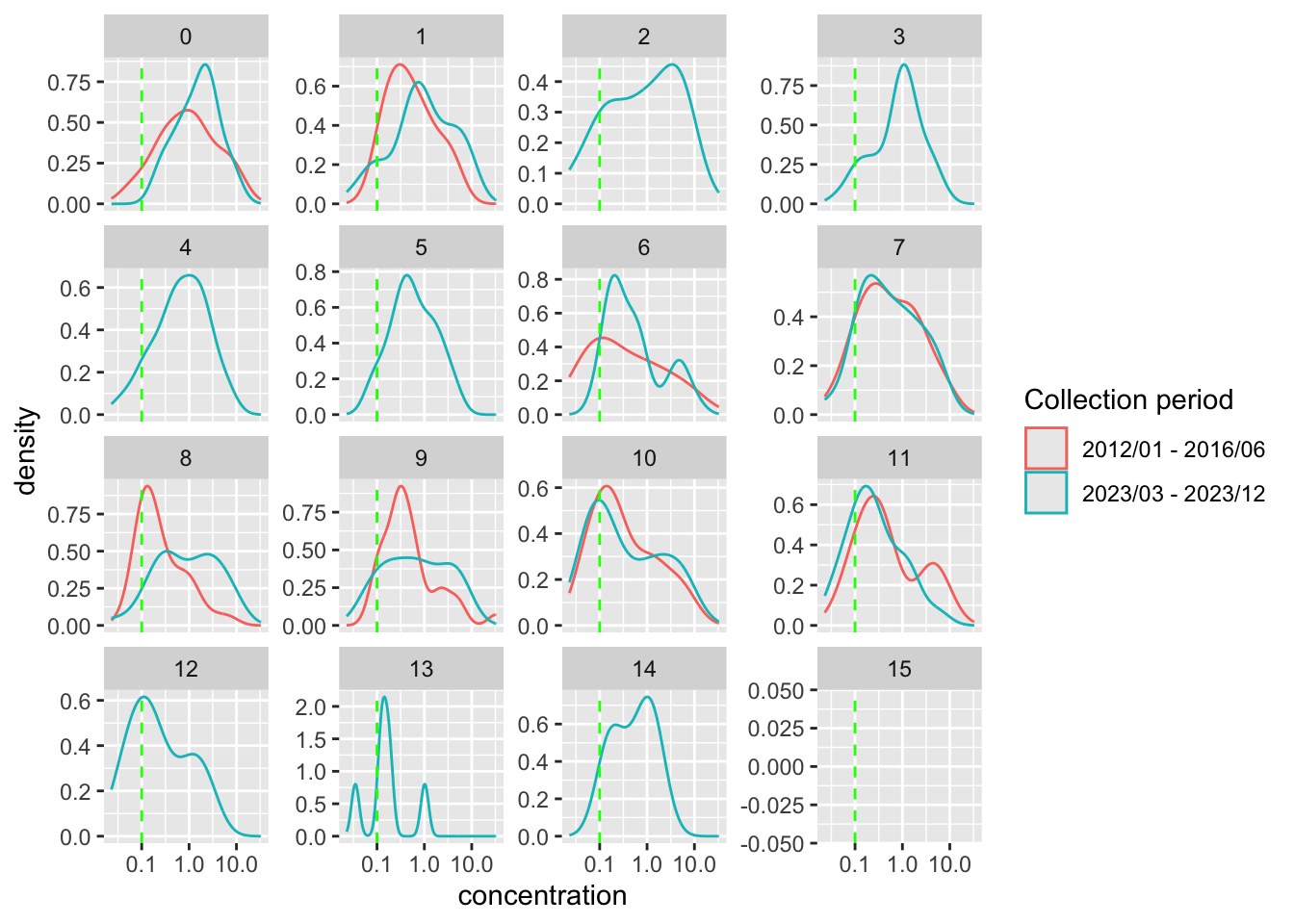
Distribution of concentration for each age group
Plot distribution of concentration stratified by age
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(
rounded_age <= 15,
dilution_factors == dilution_fct
) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_density(
aes(
x = concentration,
color = time_durr
)
) +
geom_vline(
aes(xintercept = positive_threshold),
color = "green",
linetype = "dashed"
) +
scale_x_log10()+
facet_wrap(~ rounded_age, scales = "free_y") +
labs(
color = "Collection period"
)
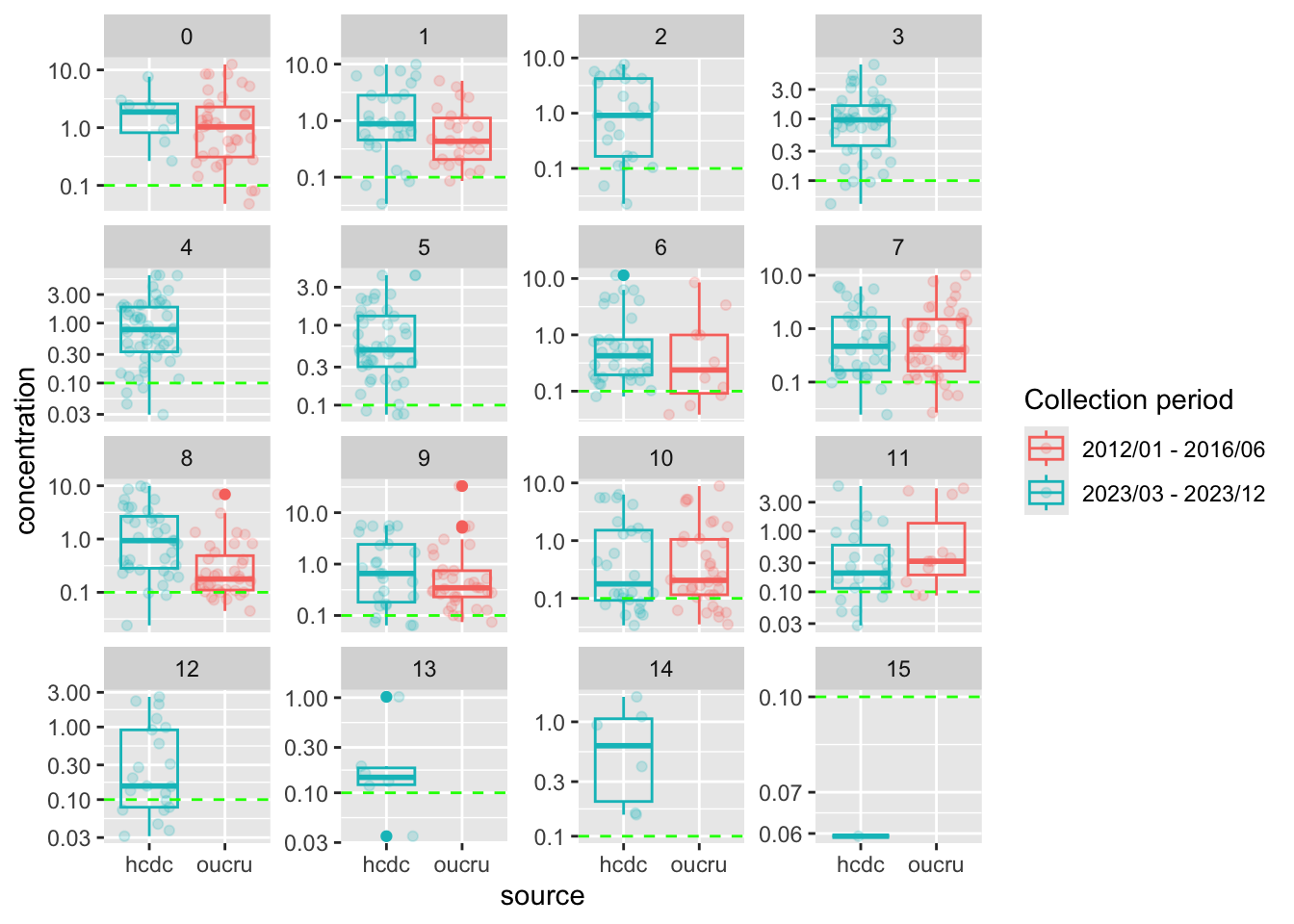
Box plot of concentration per age group
Code for box plot of concentration
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(
rounded_age <= 15,
dilution_factors == dilution_fct
) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_jitter(
aes(
x = source,
y = concentration,
color = time_durr
),
alpha = 0.2
) +
geom_boxplot(
aes(
x = source,
y = concentration,
color = time_durr
),
fill = NA
) +
geom_hline(
aes(yintercept = positive_threshold),
color = "green",
linetype = "dashed"
) +
scale_y_log10()+
facet_wrap(~ rounded_age, scales = "free_y")+
labs(
color = "Collection period"
)
Code for plotting concentration over age
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(
rounded_age <= 15,
dilution_factors == dilution_fct
) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_point(
aes(
x = age,
y = concentration,
color = time_durr
),
alpha = 0.2
) +
geom_smooth(
aes(
x = age,
y = concentration,
color = time_durr,
fill = time_durr
),
method = "loess"
) +
geom_hline(
aes(yintercept = positive_threshold),
color = "green",
linetype = "dashed"
) +
scale_y_log10() +
labs(
color = "Collection period"
) +
guides(fill = "none")`geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'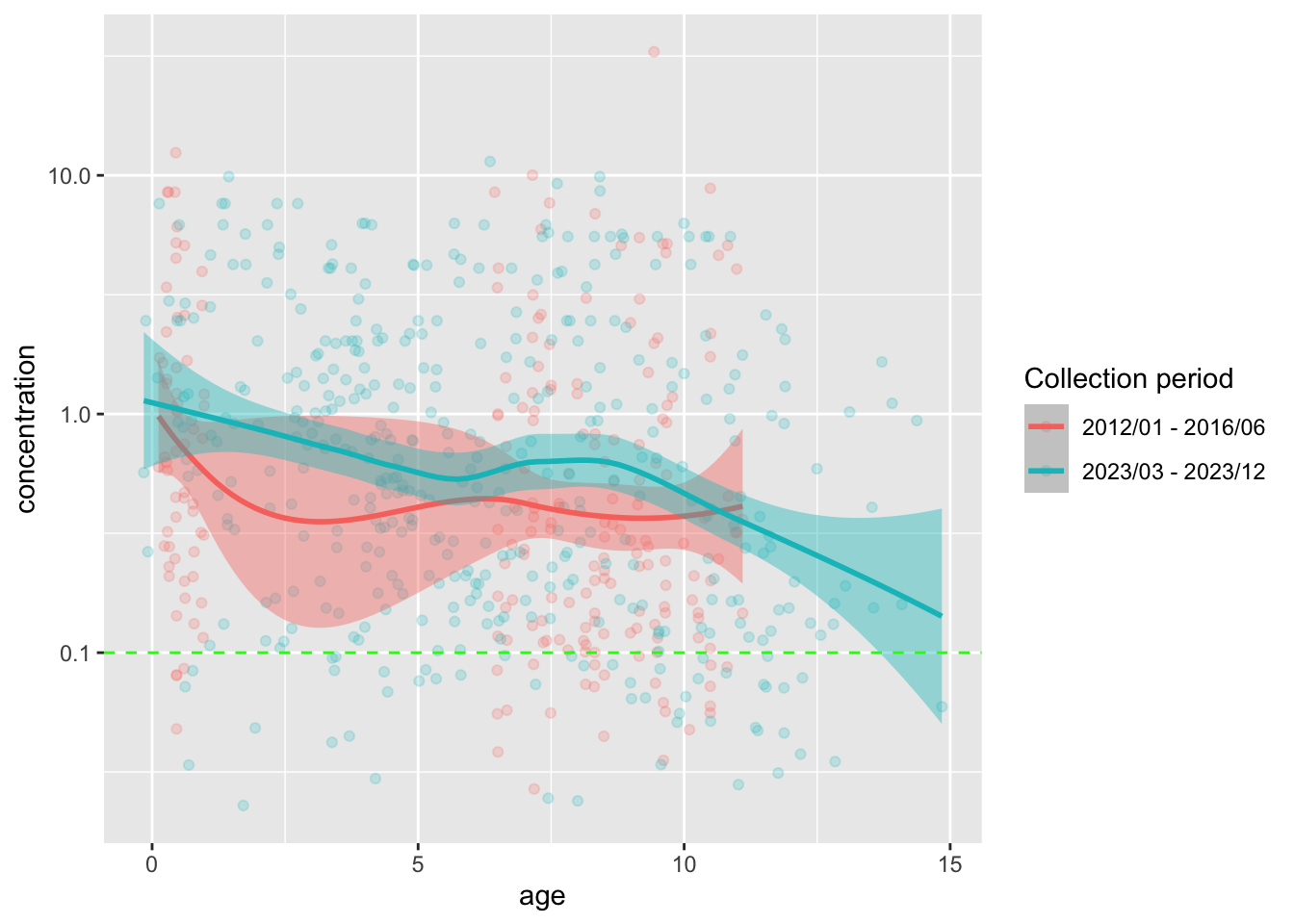
Note:
- There are no samples for age groups
3 - 5and12 - 15during the 2012-2016 collection period
The following table summarizes number of samples for each rounded age from each collection period
Check sample size for each age-group
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(
rounded_age <= 15,
dilution_factors == dilution_fct
) %>%
group_by(time_durr, rounded_age) %>%
count() %>%
pivot_wider(
names_from = time_durr,
values_from = n
) %>%
arrange(rounded_age)# A tibble: 16 × 3
# Groups: rounded_age [16]
rounded_age `2012/01 - 2016/06` `2023/03 - 2023/12`
<dbl> <int> <int>
1 0 36 10
2 1 25 39
3 2 NA 28
4 3 NA 54
5 4 NA 63
6 5 NA 46
7 6 11 41
8 7 39 37
9 8 35 42
10 9 34 30
11 10 35 31
12 11 11 25
13 12 NA 22
14 13 NA 6
15 14 NA 6
16 15 NA 1Stratified by age group
Separate the data into 2 age groups: <3 and 7-12 for comparison
Compute age group for stratification
data_by_agegrp <- preprocessed_data %>%
mutate(
age_group = case_when(
age < 3 ~ "< 3",
age >= 7 & age <= 12 ~ "7-12",
.default = NA
)
) %>%
filter(
!is.na(age_group),
dilution_factors == dilution_fct
) Perform two samples Wilcoxon test to compare distribution of concentration (on log scale) of 2 age groups (<3, 7-12) between samples from 2 collection periods
Perform wilcoxon test to compare log concentration for 2 age groups
concentration_by_agegrp <- data_by_agegrp %>%
filter(!is.na(concentration)) %>%
group_by(
age_group
) %>%
nest() %>% # divide the data.frame by each age group
mutate(
# perform t.test to compare samples from each source
# t_test = map(data,
# ~ t.test(
# log_concentration ~ source, data = .x
# )
# ),
# p_value = map_dbl(t_test, ~.x$p.value),
# perform two-sample wilcoxon test instead to compare samples from each source
wilcox = map(data,
~ t.test(
log_concentration ~ time_durr, data = .x
)
),
p_value = map_dbl(wilcox, ~.x$p.value),
# compute summary for samples from each source (HCDC and OUCRU)
dat_summary = map(data, \(dat){
dat %>%
group_by(time_durr) %>%
summarize(
median_concentration = median(concentration),
lwr = quantile(concentration, probs = 0.25),
upper = quantile(concentration, probs = 0.75)
) %>%
mutate(
label = sprintf("%.4f (%.4f–%.4f)",
median_concentration,
lwr,
upper),
.keep = "unused"
)
}
)
) %>%
unnest(
dat_summary
) %>%
pivot_wider(
names_from = time_durr,
values_from = label
)Generate the comparison table
concentration_by_agegrp %>%
select(-wilcox, -data) %>%
relocate(p_value, .after = last_col()) %>%
ungroup() %>%
gt(rowname_col = "age_group") %>%
tab_header(title = "Log(concentration) by collection period and age group") %>%
tab_style(
style = list(cell_text(weight = "bold")),
locations = list(
cells_column_labels(everything()),
cells_stub()
)
)| Log(concentration) by collection period and age group | |||
| 2012/01 - 2016/06 | 2023/03 - 2023/12 | p_value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 3 | 0.6785 (0.2746–1.6855) | 0.9333 (0.3935–2.8357) | 0.3767952 |
| 7-12 | 0.3187 (0.1287–1.0571) | 0.4078 (0.1331–1.7665) | 0.2340958 |
Note:
- The result suggests that for both age groups, there is no statistically significant difference in the
log(concentration)of samples between the 2 collection periods.
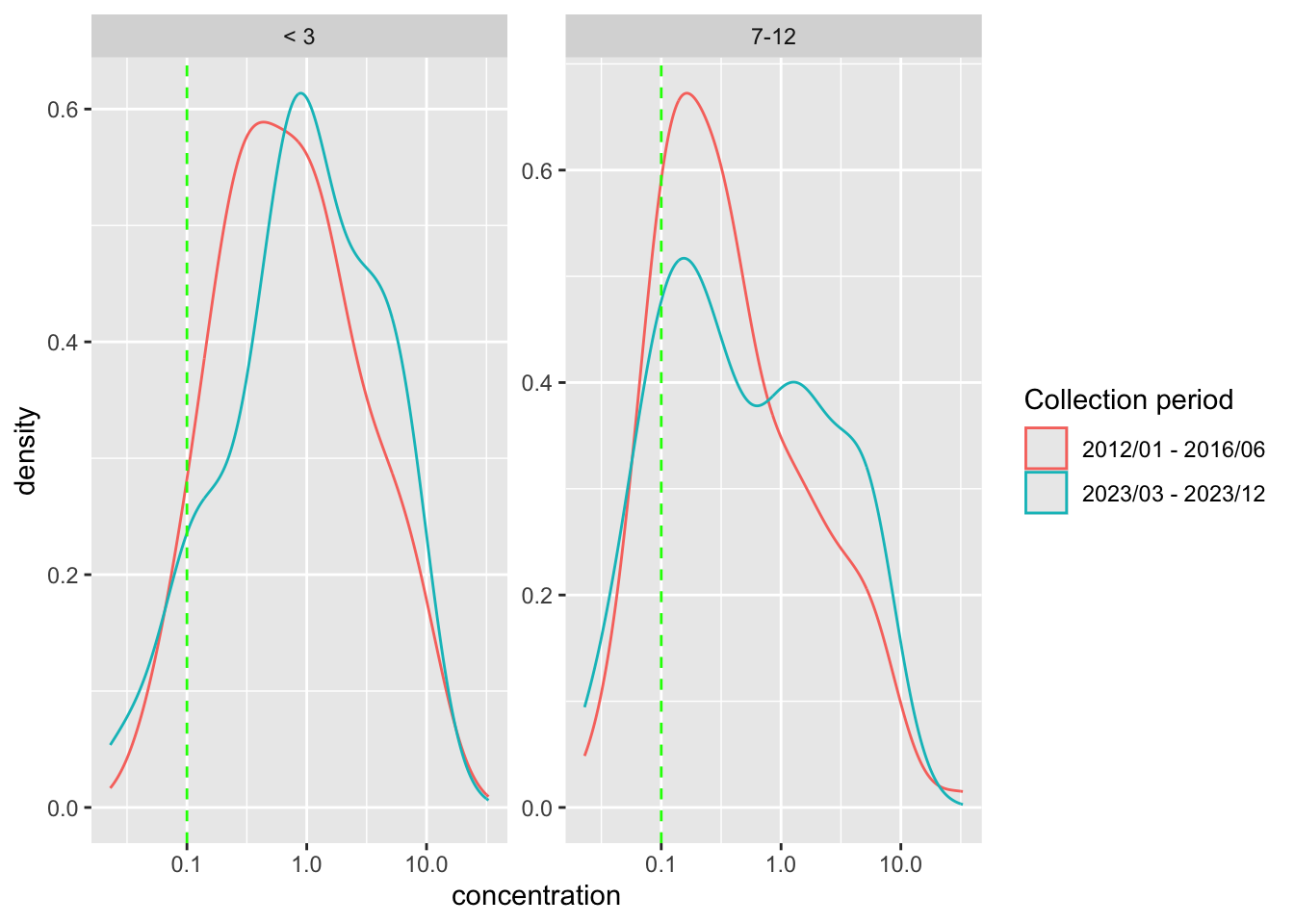
The following plots demonstrate the distribution of log(concentration)
Generate the density plot
concentration_by_agegrp %>%
unnest(data) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_density(
aes(
x = concentration,
color = time_durr
)
) +
geom_vline(
aes(xintercept = positive_threshold),
color = "green",
linetype = "dashed"
) +
scale_x_log10() +
facet_wrap(~ age_group, scales = "free_y") +
labs(
color = "Collection period"
) 
Generate the box plot
concentration_by_agegrp %>%
unnest(data) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_jitter(
aes(
x = time_durr,
y = concentration,
color = time_durr
),
alpha = 0.2
) +
geom_boxplot(
aes(
x = time_durr,
y = concentration,
color = time_durr
),
fill = NA
) +
geom_hline(
aes(yintercept = positive_threshold),
color = "green",
linetype = "dashed"
) +
scale_y_log10() +
labs(
color = "Collection period"
) +
facet_wrap(~ age_group, scales = "free_y")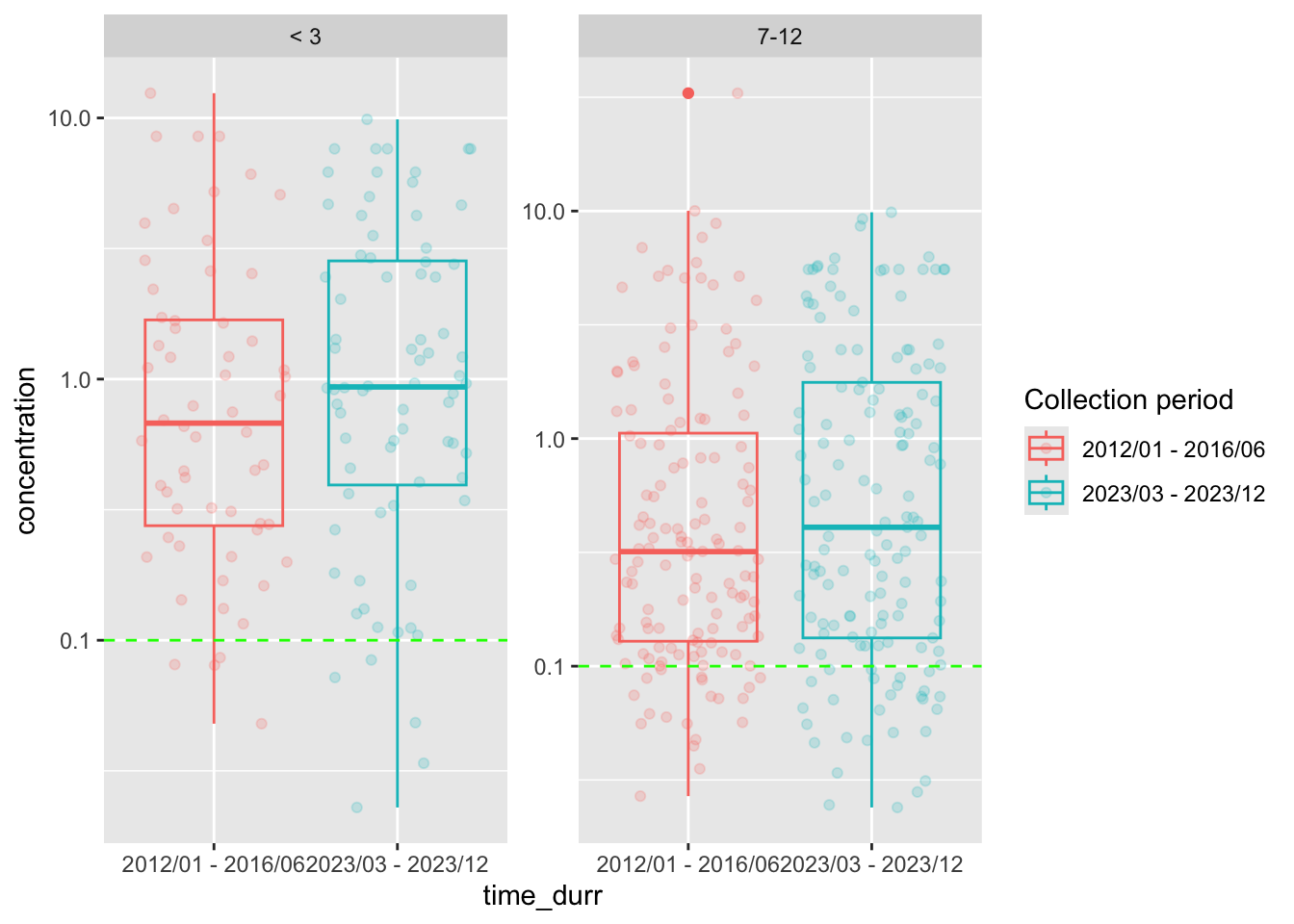
Seroprevalence
Comparison table
Compute prevalence and confidence interval
prevalence_by_agegrp <- data_by_agegrp %>%
group_by(
time_durr, age_group
) %>%
summarize(
seropositive = sum(serostatus == "positive"),
sample_size = sum(!is.na(serostatus))
) %>%
rowwise() %>%
mutate(
seroprevalence = seropositive/sample_size,
seroprevalence_ci = list(
prop.test(
x = seropositive, n = sample_size,
conf.level = 0.95)$conf.int
),
seroprevalence_lwr = seroprevalence_ci[[1]],
seroprevalence_upper = seroprevalence_ci[[2]]
) %>%
ungroup()Seroprevalence with confidence intervals
generate the table
prevalence_by_agegrp %>%
mutate(
label = sprintf("%.1f%% (%.1f–%.1f%%)",
100 * seroprevalence,
100 * seroprevalence_lwr,
100 * seroprevalence_upper)
) %>%
select(time_durr, age_group, label) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = time_durr,
values_from = label) %>%
gt(rowname_col = "age_group") %>%
tab_header(title = "Seroprevalence by collection period and age group") %>%
tab_style(
style = list(cell_text(weight = "bold")),
locations = list(
cells_column_labels(everything()),
cells_stub()
)
)| Seroprevalence by collection period and age group | ||
| 2012/01 - 2016/06 | 2023/03 - 2023/12 | |
|---|---|---|
| 7-12 | 85.8% (78.7–90.9%) | 83.4% (76.6–88.6%) |
| < 3 | 93.4% (83.3–97.9%) | 94.0% (86.9–97.5%) |
Comparison tables with p-value. Only samples from the 2 age groups <3 and 7-12 are included.
Chi-squared test
generate the summary table
library(gtsummary)
data_by_agegrp %>%
select(serostatus, time_durr) %>%
tbl_summary(
by = time_durr,
type = all_categorical() ~ "categorical",
missing = "no"
) %>%
add_p(test = everything() ~ "chisq.test") %>%
add_n() %>%
bold_labels()| Characteristic | N | 2012/01 - 2016/06 N = 2021 |
2023/03 - 2023/12 N = 2631 |
p-value2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| serostatus | 465 | >0.9 | ||
| negative | 24 (12%) | 33 (13%) | ||
| positive | 178 (88%) | 230 (87%) | ||
| 1 n (%) | ||||
| 2 Pearson’s Chi-squared test | ||||
perform Fisher exact test
prevalence_compare <- data_by_agegrp %>%
group_by(
age_group
) %>%
nest() %>% # divide the data.frame by each age group
mutate(
# perform fisher.test to compare samples from each source
fisher_test = map(data,
\(df){
tab <- table(df$serostatus, df$time_durr)
fisher.test(tab)
}
),
fisher_test_p = map_dbl(fisher_test, ~.x$p.value),
odd_ratio = map_chr(fisher_test, \(out){
sprintf("%.3f (%.3f–%.3f)",
out$estimate,
out$conf.int[1],
out$conf.int[2])
}),
# compute summary for samples from each source (HCDC and OUCRU)
dat_summary = map(data, \(dat){
dat %>%
group_by(time_durr) %>%
summarize(
label = paste0(sum(serostatus == "positive"), "/", n())
)
}
)
) %>%
unnest(
dat_summary
) %>%
ungroup() %>%
pivot_wider(
names_from = time_durr,
values_from = label
)Check the negative-positive counts for each age group
map(prevalence_compare$data,
\(df){
table(df$serostatus, df$time_durr)
})[[1]]
2012/01 - 2016/06 2023/03 - 2023/12
negative 4 6
positive 57 94
[[2]]
2012/01 - 2016/06 2023/03 - 2023/12
negative 20 27
positive 121 136Comparison table with p-value from the Fisher exact test
generate the table
prevalence_compare %>%
select(-data, -fisher_test) %>%
relocate(odd_ratio, fisher_test_p, .after = last_col()) %>%
rename(
p_val = fisher_test_p,
`2023/03 - 2023/12 (pos/tot)` = `2023/03 - 2023/12`,
`2012/01 - 2016/06 (pos/tot)` = `2012/01 - 2016/06`,
`Odd ratio (95% CI)` = odd_ratio
) %>%
gt(rowname_col = "age_group") %>%
tab_header(title = "Compare prevalence by collection period and age group") %>%
tab_style(
style = list(cell_text(weight = "bold")),
locations = list(
cells_column_labels(everything()),
cells_stub()
)
) %>%
fmt_number(
columns = where(is.numeric),
decimals = 4
)| Compare prevalence by collection period and age group | ||||
| 2012/01 - 2016/06 (pos/tot) | 2023/03 - 2023/12 (pos/tot) | Odd ratio (95% CI) | p_val | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 3 | 57/61 | 94/100 | 1.099 (0.218–4.862) | 1.0000 |
| 7-12 | 121/141 | 136/163 | 0.833 (0.420–1.631) | 0.6344 |
Age stratified seroprevalence
Helper function to compute age-stratified aggregated seroprev
compute_seroprev <- function(data, age_lim, dilution_fct, group_var){
if(!is.null(group_var)){
out <- data %>%
filter(age<=age_lim, dilution_factors == dilution_fct) %>%
mutate(
serostatus = if_else(serostatus == "positive", 1, 0),
!! group_var := factor(.data[[group_var]])
) %>%
group_by(rounded_age, .data[[group_var]]) %>%
summarize(
pos = sum(serostatus, na.rm = TRUE),
tot = n(),
neg = tot - pos,
seroprev = sum(serostatus, na.rm = TRUE)/n()
) %>%
ungroup()
}else{
out <- data %>%
filter(age<=age_lim, dilution_factors == dilution_fct) %>%
mutate(
serostatus = if_else(serostatus == "positive", 1, 0)
) %>%
group_by(rounded_age) %>%
summarize(
pos = sum(serostatus, na.rm = TRUE),
tot = n(),
neg = tot - pos,
seroprev = sum(serostatus, na.rm = TRUE)/n()
) %>%
ungroup()
}
out
}Check whether there is a difference in seroprevalence between:
samples from the 2 collection periods
female and male samples
Model stratified by collection period
# ----- Model with smoothing stratified by collection period ------
seroprev_mod_coll <- preprocessed_data %>%
compute_seroprev(age_lim = 15, dilution_fct = dilution_fct, group_var = "time_durr") %>%
gam(cbind(pos, neg) ~ s(rounded_age, bs = "bs", by = time_durr) + time_durr, data = ., family=binomial(link = "logit"))
summary(seroprev_mod_coll)
Family: binomial
Link function: logit
Formula:
cbind(pos, neg) ~ s(rounded_age, bs = "bs", by = time_durr) +
time_durr
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 1.8778 0.2000 9.389 <2e-16 ***
time_durr2023/03 - 2023/12 0.1184 0.2581 0.459 0.646
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df Chi.sq p-value
s(rounded_age):time_durr2012/01 - 2016/06 1.000 1.000 2.369 0.123779
s(rounded_age):time_durr2023/03 - 2023/12 2.854 3.555 19.386 0.000406 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
R-sq.(adj) = 0.355 Deviance explained = 54.4%
UBRE = 0.33797 Scale est. = 1 n = 24Model stratified by gender
# ----- Model with smoothing stratified by gender ------
seroprev_mod_gender <- preprocessed_data %>%
compute_seroprev(age_lim = 15, dilution_fct = dilution_fct, group_var = "gender") %>%
gam(cbind(pos, neg) ~ s(rounded_age, bs = "bs", by = gender) + gender, data = ., family=binomial(link = "logit"))
summary(seroprev_mod_gender)
Family: binomial
Link function: logit
Formula:
cbind(pos, neg) ~ s(rounded_age, bs = "bs", by = gender) + gender
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 2.2626 0.2973 7.611 2.73e-14 ***
gendermale -0.3301 0.3328 -0.992 0.321
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df Chi.sq p-value
s(rounded_age):genderfemale 1.000 1.000 0.044 0.835
s(rounded_age):gendermale 2.809 3.503 24.448 4.35e-05 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
R-sq.(adj) = 0.439 Deviance explained = 54.3%
UBRE = 0.19118 Scale est. = 1 n = 29Model without stratification for smoothing
# ----- Baseline model (no stratification) ------
seroprev_mod <- preprocessed_data %>%
compute_seroprev(age_lim = 15, dilution_fct = dilution_fct, group_var = NULL) %>%
gam(cbind(pos, neg) ~ s(rounded_age, bs = "bs"), data = ., family=binomial(link = "logit"))
summary(seroprev_mod)
Family: binomial
Link function: logit
Formula:
cbind(pos, neg) ~ s(rounded_age, bs = "bs")
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 1.9015 0.1342 14.17 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df Chi.sq p-value
s(rounded_age) 1.669 2.087 18.36 0.000139 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
R-sq.(adj) = 0.478 Deviance explained = 61.5%
UBRE = 0.089952 Scale est. = 1 n = 16Note:
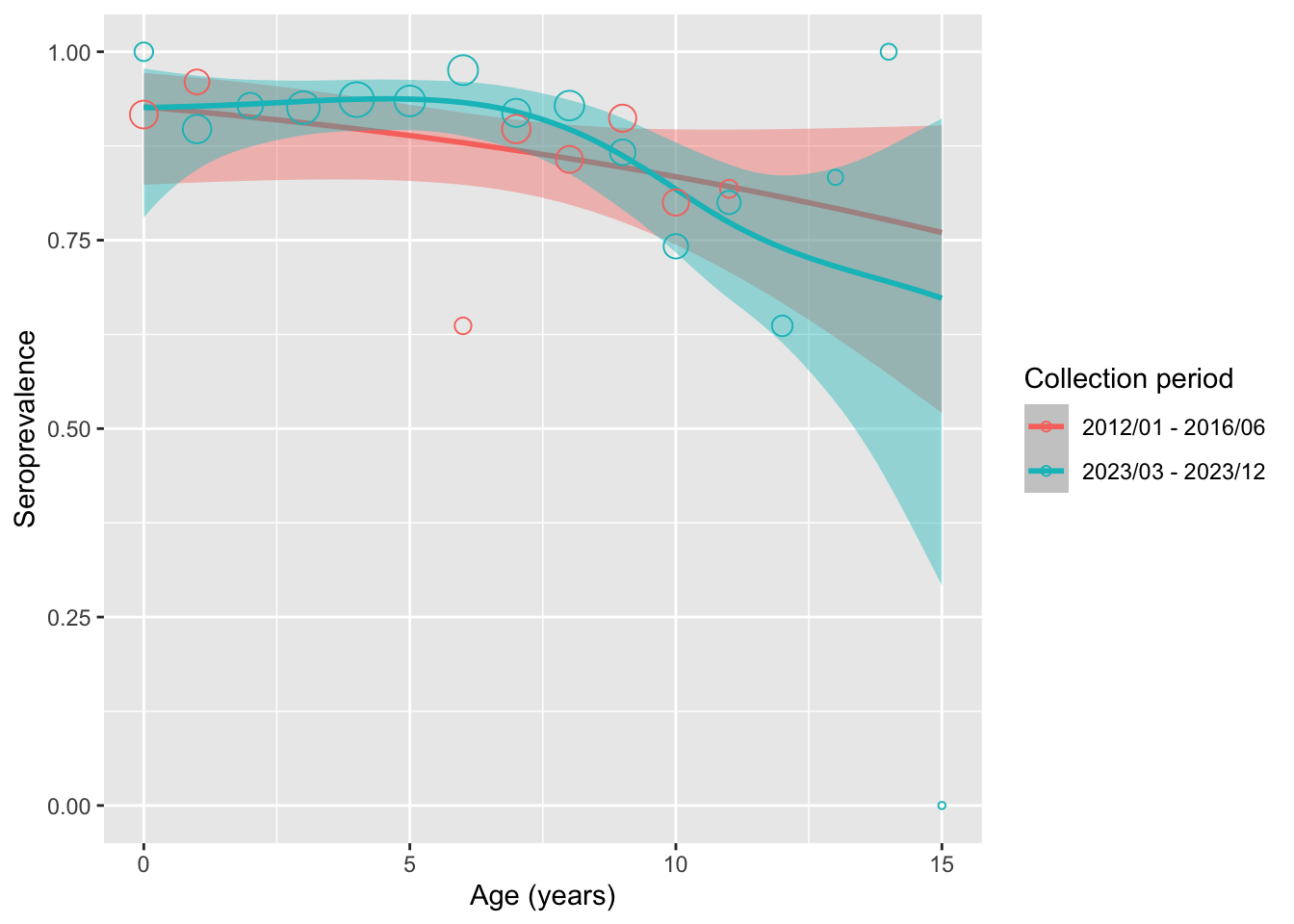
The result from model stratified by (sample) source suggests that:
- There’s no statistically significant difference in seroprevalence between the samples from these 2 sampling period
The result from model stratified by gender suggests that:
- There’s no statistically significant difference in seroprevalence between male and female samples
However, it may be due to the fact that the sample size for the earlier collection period (using OUCRU samples) is quite small and we don’t have any data for several age groups (3-6, 11-14)
Another issue is that there is an imbalance in the number of male vs female samples during later collection period (male:female ratio is 13.58:1)
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(dilution_factors == dilution_fct) %>%
group_by(source, time_durr, gender) %>%
count()# A tibble: 4 × 4
# Groups: source, time_durr, gender [4]
source time_durr gender n
<chr> <chr> <chr> <int>
1 hcdc 2023/03 - 2023/12 female 33
2 hcdc 2023/03 - 2023/12 male 448
3 oucru 2012/01 - 2016/06 female 241
4 oucru 2012/01 - 2016/06 male 247Quick visualization
Visualize the model for collection period/gender stratified smoothing
Helper function to visualize model with confidence interval
visualize_pred <- function(data, mod, group_var, ci = 0.95, length_out = 100, cex = 20){
if(!is.null(group_var)){
newdata <- data %>%
select({{group_var}}) %>%
distinct() %>%
crossing(
rounded_age = seq(min(data$rounded_age), max(data$rounded_age), length.out = length_out)
)
}else{
newdata <- data.frame(
rounded_age = seq(min(data$rounded_age), max(data$rounded_age), length.out = length_out)
)
}
linkinv <- mod$family$linkinv
p <- (1 - ci) / 2
n <- mod$df.residual
out <- predict(
mod,
newdata = newdata, se.fit = TRUE) %>%
as_tibble() %>%
select(fit, se.fit) %>%
mutate(
rounded_age = newdata$rounded_age,
lower = linkinv(fit + qt(p, n) * se.fit),
upper = linkinv(fit + qt(1 - p, n) * se.fit),
fit = linkinv(fit)
)
if(!is.null(group_var)){
out <- out %>%
mutate(
!! group_var := newdata[[group_var]]
)
}
ggplot() +
geom_smooth(
aes(
x = rounded_age, y = fit,
ymin = lower, ymax = upper,
color = if(!is.null(group_var)) factor(.data[[group_var]]) else "cornflowerblue",
fill = if(!is.null(group_var)) factor(.data[[group_var]]) else "cornflowerblue"
),
data = out,
stat = "identity"
) +
geom_point(
aes(
x = rounded_age, y = seroprev,
size = cex*pos/max(tot),
color = if(!is.null(group_var)) factor(.data[[group_var]]) else "black",
fill = if(!is.null(group_var)) factor(.data[[group_var]]) else "grey"
),
shape = 1,
data = data
) +
guides(size = "none", fill="none") +
labs(x = "Age (years)",
y = "Seroprevalence",
color = if(!is.null(group_var)) str_to_title(group_var) else "")
}preprocessed_data %>%
compute_seroprev(age_lim = 15, dilution_fct = dilution_fct, group_var = "time_durr") %>%
visualize_pred(mod = seroprev_mod_coll, group_var = "time_durr") +
labs(
color = "Collection period"
)
Imbalance in sample size causes larger CI interval for female
preprocessed_data %>%
compute_seroprev(age_lim = 15, dilution_fct = dilution_fct, group_var = "gender") %>%
visualize_pred(mod = seroprev_mod_gender, group_var = "gender")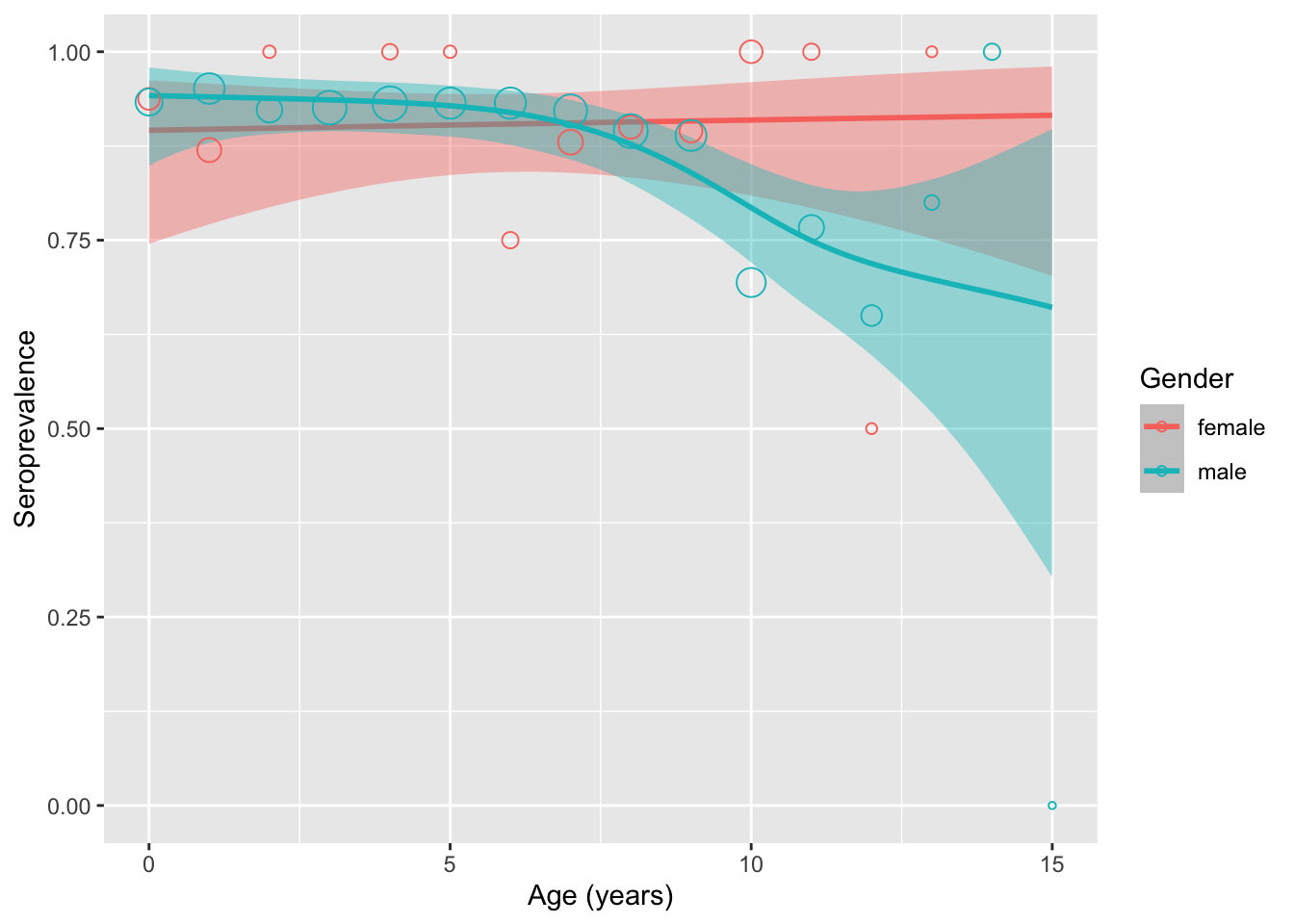
HCDC samples - a closer look
Seroprevalence - FOI by age
Age-stratified seroprevalence across HCDC samples
library(serosv)
# use rounded age
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(
source == "hcdc",
rounded_age <= 15,
dilution_factors == dilution_fct,
!is.na(serostatus)
) %>%
select(rounded_age, serostatus) %>%
mutate(
status = if_else(serostatus == "positive", 1, 0)
) %>%
rename(
age = rounded_age
) %>%
penalized_spline_model(s = "tp", framework = "pl") %>%
plot()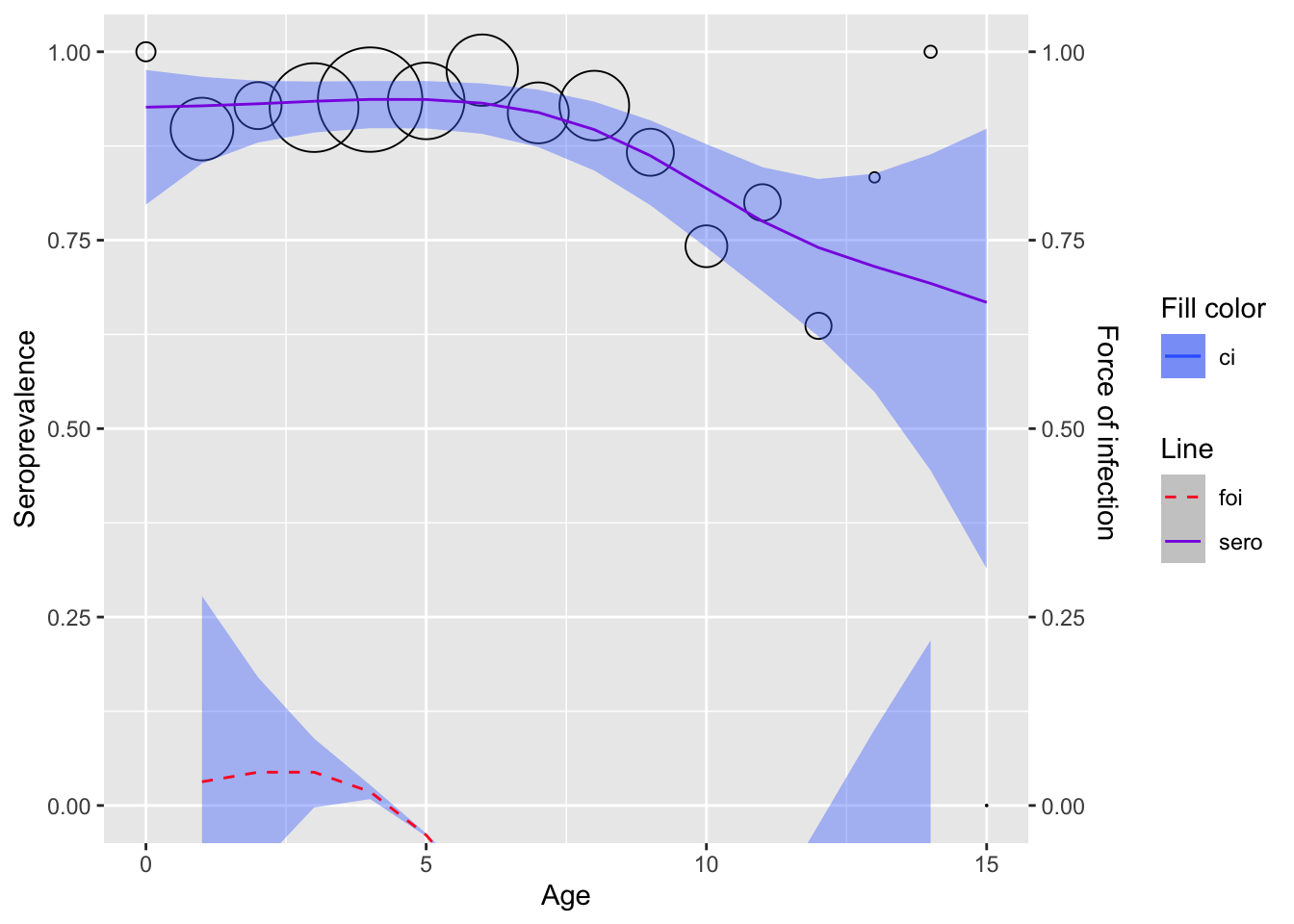
Sample distribution by district
preprocessed_data %>%
filter(source == "hcdc") %>%
generate_district_plots() %>%
pull(age_gender_plot)[[1]]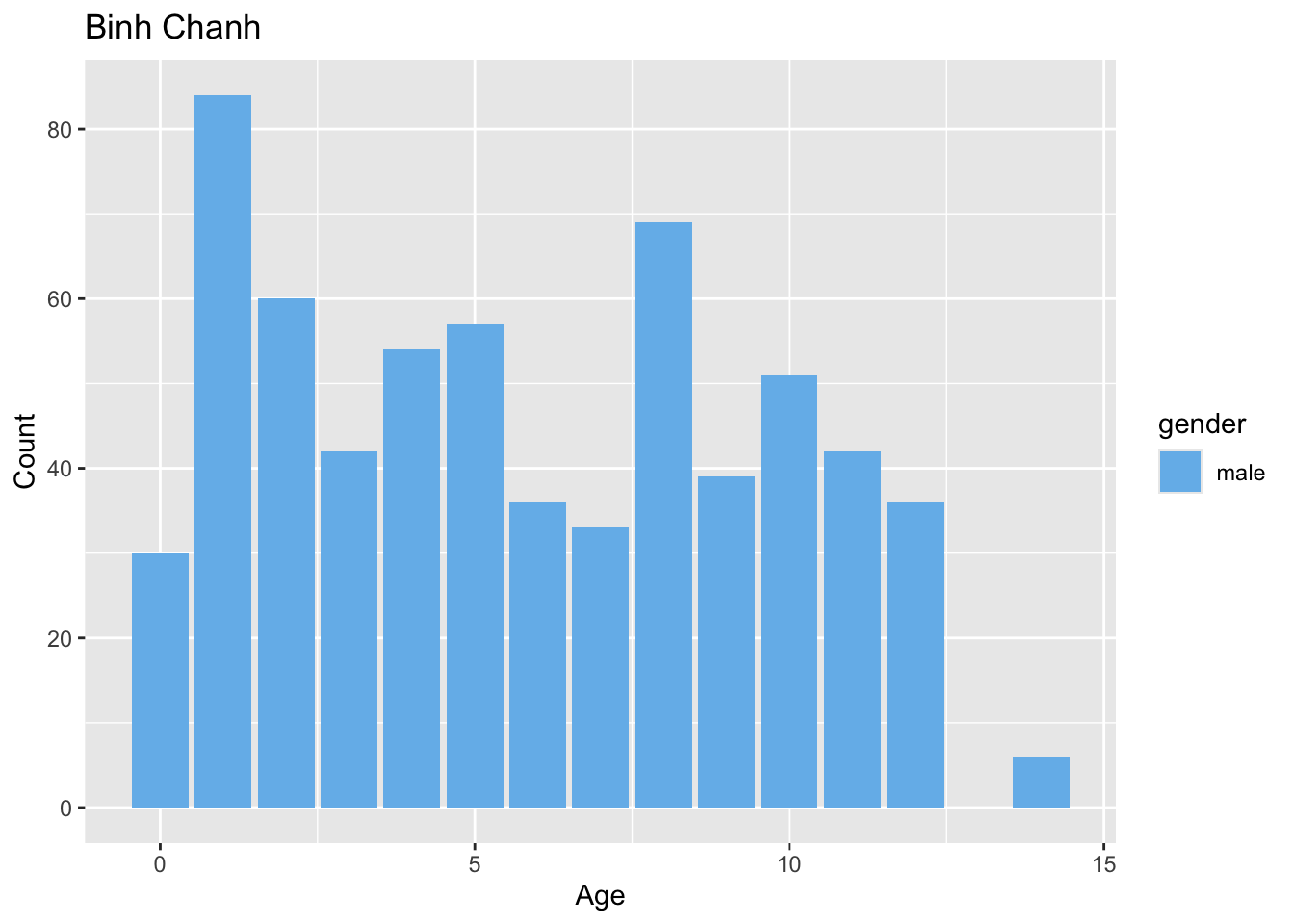
[[2]]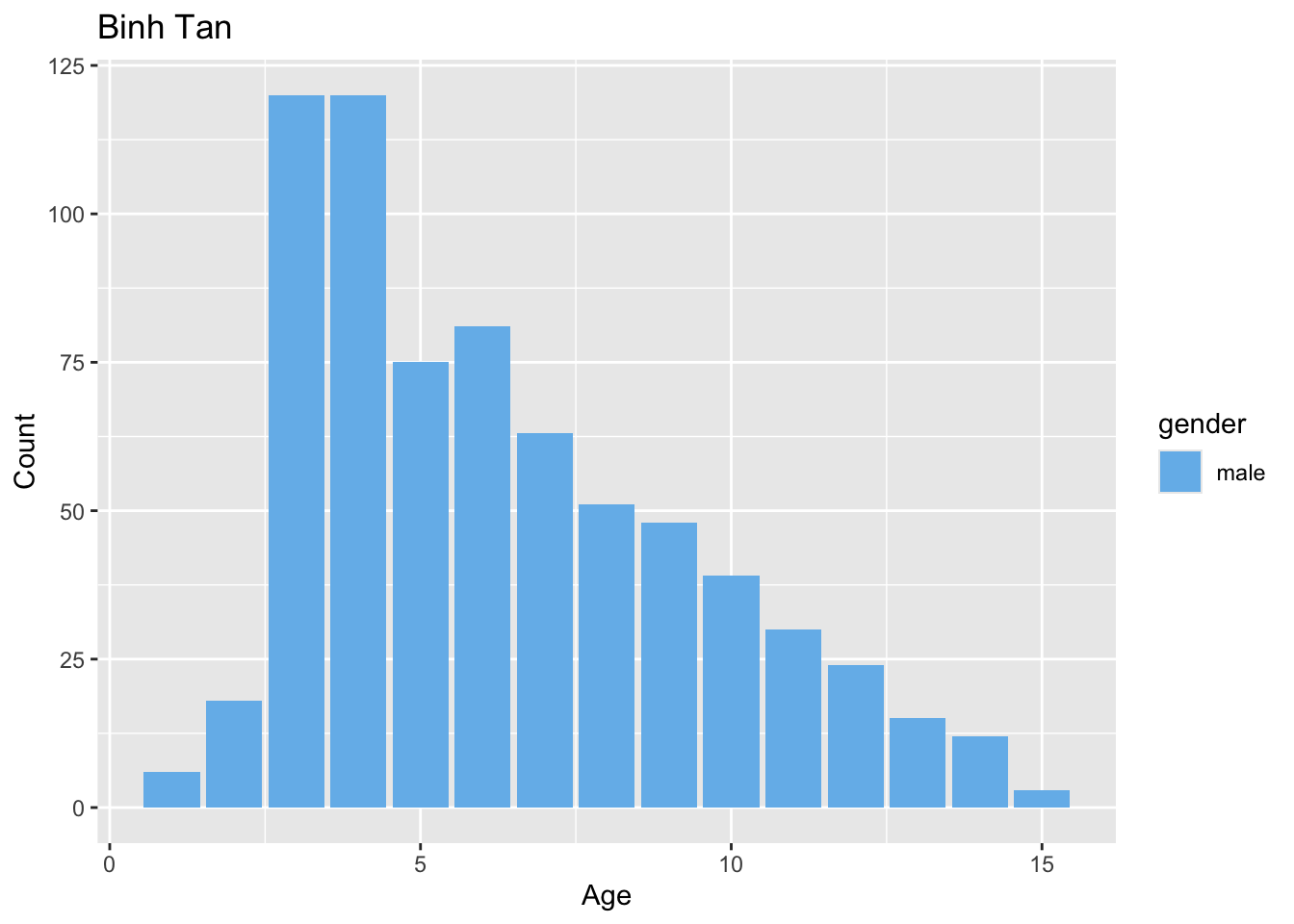
[[3]]
[[4]]